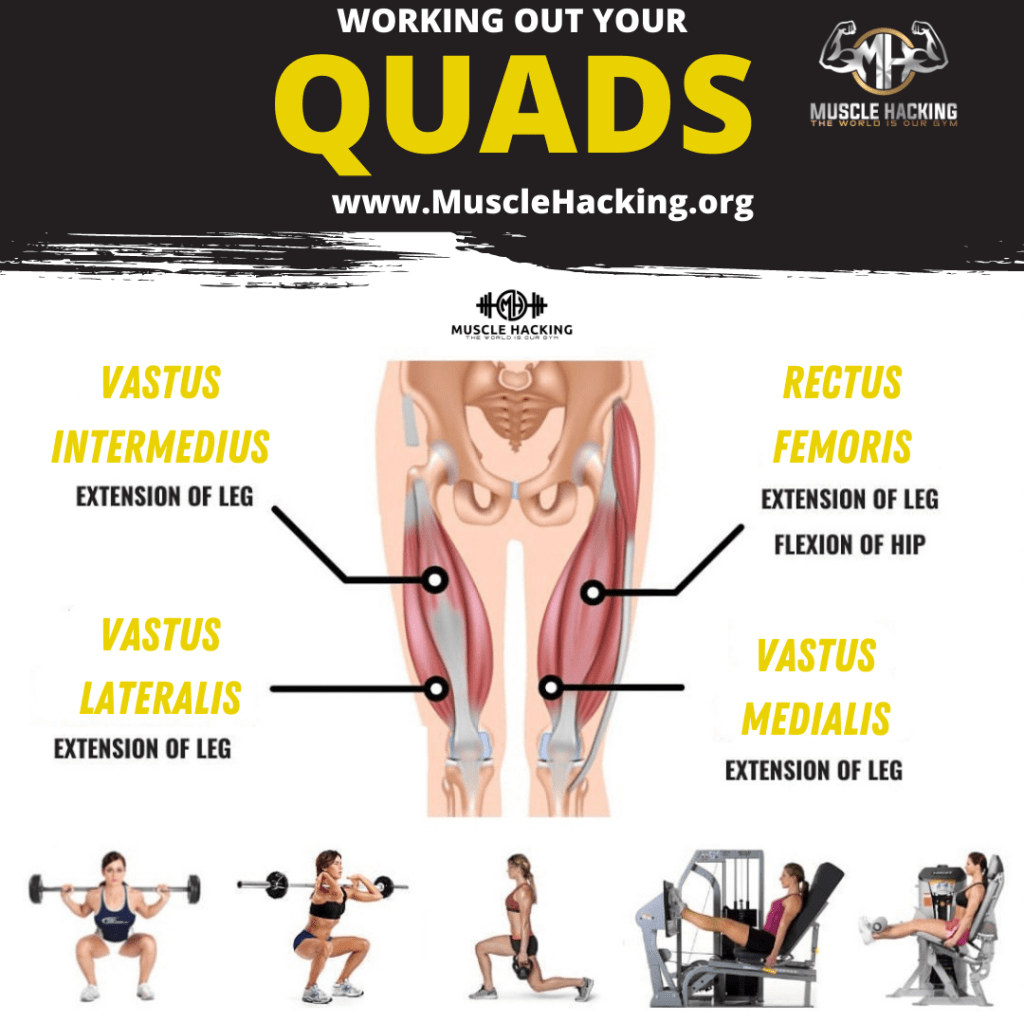
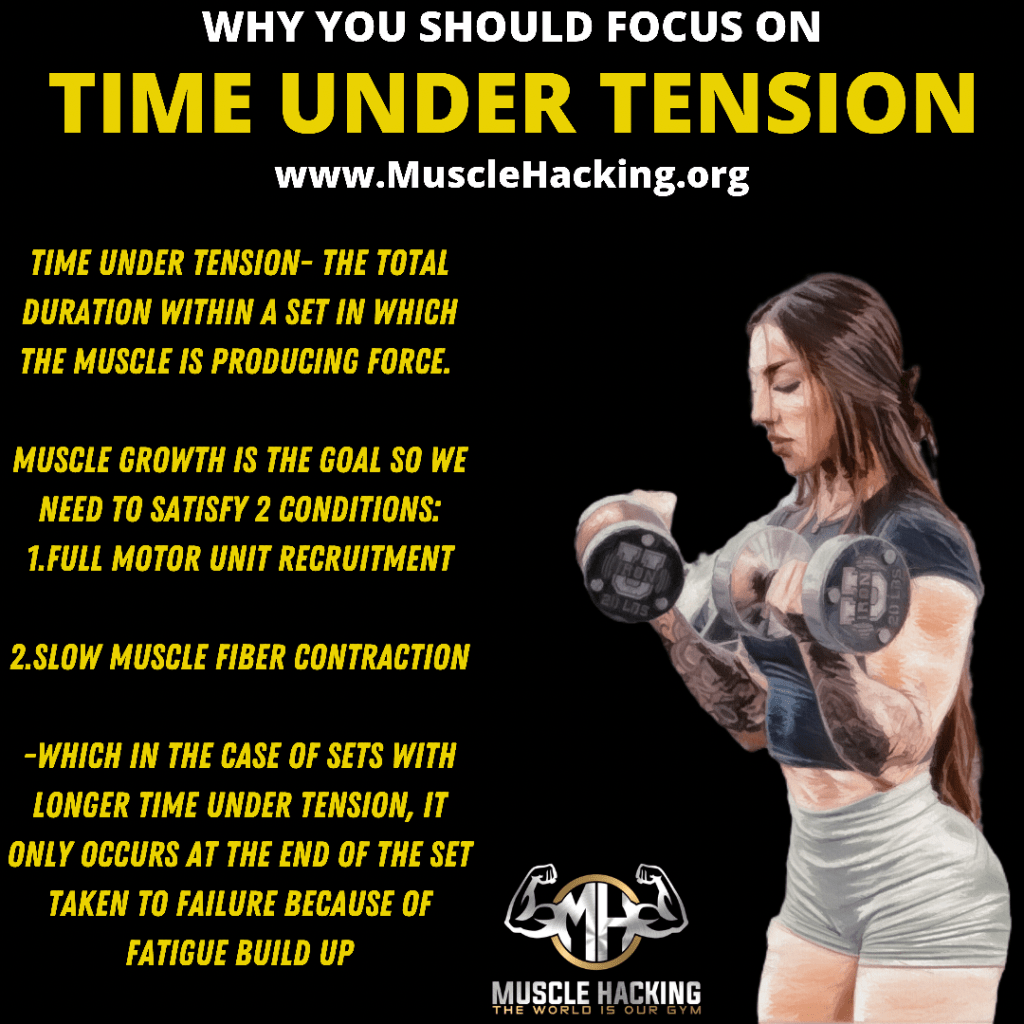
♠️Does alcohol consumption affect muscle hypertrophy♠️
🔹Exercise and protein intake are the main factors that create muscle protein synthesis (the main process driving muscle adaptations, such as growth).
🔹It has been documented that athletes are more inclined to consume excessive amounts of alcohol, especially as part of binge-drinking practices in team sports. Can these binges affect muscle protein synthesis?
🔹There was a case study that researched on the the effects of post-exercise alcohol consumption on protein synthesis rates in healthy young subjects who work out regularly. The subjects first performed combined resistance and endurance exercises in order to mimic team sports. During an 8 hours of recovery, subjects consumed either:
-25 grams of protein
-25 grams of protein and 12 standard alcoholic drinks
-25 grams of carbohydrate and 12 standard alcoholic drinks
🔹The alcohol intake ended up reducing the post-exercise muscle protein synthesis rates. But the post-exercise muscle protein synthesis rates were still elevated compared to the rest periods, even when alcohol was ingested.
🔹So what this means is that even when you know that you will consume large amounts of alcohol afterwards, it is not an excuse to skip your training session.
⚠️Keep in mind that the subjects received a large amount of alcohol (i.e. 12 drinks). The amount of alcohol in the study was to mimic the binge drinking practices of sports players. If the alcohol consumption was lower, there would be much less of a effect.
🔹The conclusion is that consumption of large amounts of alcohol after exercise lowers protein synthesis.
Resources: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24533082/